Explore various diseases and treatments
At Dr.piles, we provide specialized care for hemorrhoids, using gentle and effective homeopathic remedies tailored to the unique symptoms and needs of each patient. Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are swollen veins in the lower rectum and anus. Our approach targets the root causes, offering long-term relief without invasive procedures. Homeopathy strengthens the body’s natural healing process while addressing symptoms such as pain, swelling, and bleeding.
Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are swollen veins in the lower part of the anus and rectum. When the walls of these vessels stretch, they can become irritated. Older age, pregnancy, and constipation can cause piles. Lifestyle changes, such as eating more fiber and exercising, can help relieve symptoms and lower the risk of future hemorrhoids.
In many cases, simple measures will alleviate symptoms while hemorrhoids heal on their own. However, medication or surgery may be necessary in some instances.
Hemorrhoid medications come in various forms, including suppositories, ointments, and pads. A person can usually buy them over the counter.
If home remedies do not improve hemorrhoids, a person may need further treatment. Nonsurgical options include:Rubber band ligation: This outpatient procedure for internal hemorrhoids involves placing an elastic band on the base of the hemorrhoid to block its blood supply. The hemorrhoid will either shrink or fall off.Sclerotherapy: During this procedure, doctors inject a liquid into an internal hemorrhoid. This produces a scar that cuts off the blood supply to the hemorrhoid, causing it to shrink.Infrared photocoagulation: Shining infrared light toward an internal hemorrhoid heats the area, causing scar tissue to form. This blocks the hemorrhoid’s blood supply and reduces its size.Electrocoagulation: Doctors send a low electric current into a hemorrhoid to create scarring. This scar tissue cuts off the blood supply, leading the hemorrhoid to shrink.A doctor will usually carry out these procedures while a person is under local anesthesia.
Surgery may involve the complete removal of external hemorrhoids or prolapsed internal hemorrhoids. This procedure is known as a hemorrhoidectomy.Alternatively, a doctor or surgeon may staple a prolapsed hemorrhoid back into place in the anus.During these procedures, a patient may receive a spinal block, local, or general anesthesia.
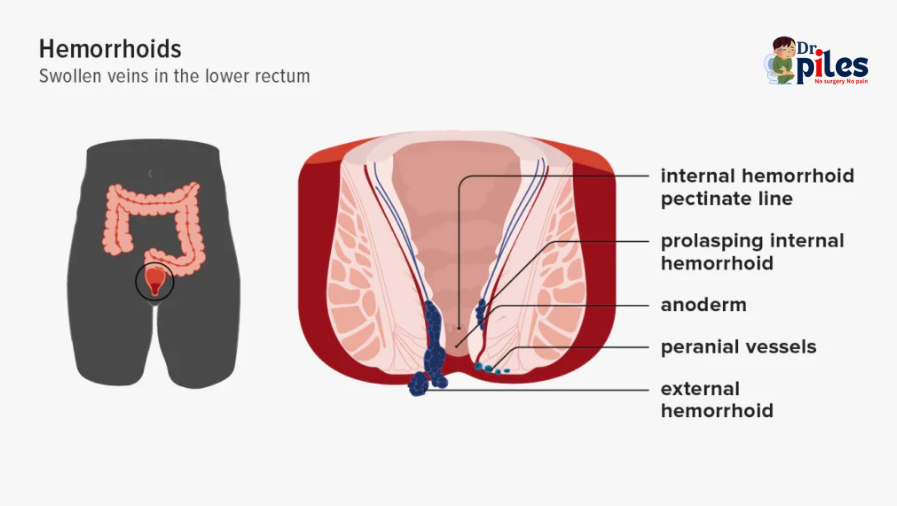
Hemorrhoids can be either internal or external. Healthcare professionals use a grading system to describe internal hemorrhoids based on whether they remain in the rectum or protrude out of the anus.
Internal hemorrhoids occur inside the rectum and are not visible from the outside. They are typically painless. Often, rectal bleeding is the first sign of internal hemorrhoids.If an internal hemorrhoid protrudes through the anus, it’s called a prolapsed hemorrhoid. This condition may be due to a weakening of the muscles around the anus and can be painful.Healthcare professionals grade internal hemorrhoids from 1 to 4 depending on the degree of prolapse:Grade 1: Hemorrhoids remain in the rectum without prolapsing.Grade 2: Hemorrhoids prolapse when a person passes stool, then return inside on their own.Grade 3: Hemorrhoids are prolapsed and require pushing back in.Grade 4: Hemorrhoids are prolapsed and will not go back inside.
External hemorrhoids occur in the skin around the anus and are, therefore, visible. There are more sensitive nerves in this part of the body, so external hemorrhoids can be very painful. Straining when passing stool may cause external or internal hemorrhoids to bleed.
A doctor will likely ask about a person’s medical history and perform a physical examination and other tests to check for hemorrhoids. They will examine the area surrounding the anus for external hemorrhoids, which involves looking for lumps, small tears in the anus, irritated skin, and prolapsed internal hemorrhoids. They may also perform a digital rectal exam to diagnose internal hemorrhoids. This involves manually inspecting the anus using a gloved, lubricated finger to check for blood, sensitivity, and lumps. If a doctor does not find internal hemorrhoids with a digital rectal exam, they may use a small device called an anoscope to check the anal and rectal lining. They may be able to view internal hemorrhoids as bulges through the device.
Lifestyle changes can help lower the risk of hemorrhoids. These include:Eating a healthy diet: Eating plenty of foods rich in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help keep stools soft. Taking OTC fiber supplements and staying hydrated can also ease constipation.Avoiding straining: A person should try not to strain when using the toilet. Straining puts pressure on the veins in the lower rectum.Going to the bathroom when necessary: It is best to avoid waiting to use the toilet. The longer a person waits, the drier the stools will be.Getting regular physical activity: Exercise helps stool move through the bowel, making bowel movements more regular.Maintaining a moderate body weight: Being overweight increases the risk of hemorrhoids.
Hemorrhoid symptoms often resolve on their own with conservative treatment, although there is a 10–50% chance they will return over 5 years. The chance of hemorrhoids returning after surgery is less than 5%.Complications can sometimes occur, such as:bleedingstrangulated hemorrhoid — when muscles around the anus block blood supply to a prolapsed hemorrhoidanemiablood clotsinfectionurinary retention
Anyone with the following symptoms should seek immediate medical help:persistent or heavy bleeding, with or without painpus leaking from hemorrhoidsfeversevere pain.It is important for a person to talk with a doctor if hemorrhoids show no improvement after a week or if new hemorrhoids keep forming. Besides hemorrhoids, conditions such as colorectal and anal cancers can cause bleeding from the rectum.